Trading vs Investing - What's the right fit for you?

In the equity market, there are two different types of players- investors and traders. These names are frequently thought to mean the same thing. This is a false notion and when discussing money-making in the stock market, it is important to have the basics right. There are significant differences between the two. Investing and trading are two distinct approaches to participating in the financial markets with the goal of generating returns. Although they may seem alike to a novice, they are in fact vastly different from each other.
Let us look at the two separately to understand the differences between them.
What is Investing?
Investing involves the allocation of funds for an extended period of time, typically several years, with the goal of building wealth or capital appreciation over the long term. Investors typically focus on purchasing securities that they believe will appreciate in value and generate income, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
The aim of an investor is to create a balanced portfolio of different stocks and bonds that give returns through an increase in value as well as dividends or interest income. This enables him or her to attain financial security. As a result, investors do not sell their holdings regularly. It is only in case of an emergency or when the stock has met its targets. The goal is to hold onto these assets for a long time, allowing the investment to grow and compound over time. Investing requires a longer-term perspective and a willingness to weather short-term market volatility in order to achieve stable returns.
Different Investing Techniques
- Value Investing: It involves finding undervalued companies with strong fundamentals, with the aim of buying low and selling high. This approach focuses on analyzing a company's financial statements, management quality, and industry conditions to determine if it is undervalued and has the potential for long-term growth. Value investors look for stocks that are trading at a lower price compared to their intrinsic value, with the expectation that the market will eventually recognize their true worth and drive up the stock price.
- Growth Investing: Growth investing is focused on buying stocks of companies expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to the market. These companies have a high growth potential and a track record of revenue and earnings growth, regardless of their current valuation.
- Momentum Investing: Momentum investing is a strategy that involves buying securities that have had strong past performance, with the expectation that this trend will continue. It is based on the belief that securities that have been performing well are more likely to continue doing so.
- Index Investing: It is a passive investment strategy where portfolios mirror the composition of a market index, such as the Nifty 50, to track the overall performance of a market or sector. The goal is to achieve returns similar to the market, with lower costs and less management than actively managed portfolios.
- Dividend Investing: This investment strategy focuses on buying stocks of companies that pay regular dividends, with the goal of generating a steady income stream from the dividends. It prioritizes income over capital appreciation and seeks to invest in financially stable, established companies with a history of consistently paying dividends.
What is Trading?
Trading, on the other hand, is a more active and shorter-term approach to the financial markets. Traders aim to make profits by exploiting short-term price fluctuations in financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, or derivatives. So, they essentially take advantage of volatility.
Traders use technical analysis with chart-based techniques and market research to make quick, informed decisions on when to buy and sell securities. Trading requires close monitoring of market conditions, a willingness to take on greater risk, and a more nimble approach to decision-making.
Different Trading Techniques
- Day Trading: Day trading or Intraday trading involves buying and selling securities within a single trading day to take advantage of short-term price movements. Day traders seek to make profits from small price changes and usually close their positions by the end of the day to minimize market risk. This style of trading requires a high level of attention and rapid decision-making and is typically suited for experienced traders.
- Swing Trading: In this trading strategy, traders hold securities for a few days to several weeks to take advantage of intermediate-term price movements. The goal is to capitalize on larger price movements than those captured in day trading, but without the longer-term commitment of a position trade. Swing traders use technical analysis and other tools to identify trends and make informed buy and sell decisions. This style of trading can be less stressful and time-consuming than day trading, but also requires a good understanding of market movements and patterns.
- Position Trading: It involves holding securities for several months for the best selling opportunities within this span to gain from. The goal is to capitalize on major trends and fundamental changes in the market and to achieve greater returns over a relatively long period of time. Position traders use a combination of fundamental and technical analysis to identify and select stocks, and to determine the best time to buy and sell.
- Scalping: Scalping is a fast-paced, high-volume trading style that seeks to make many small profits on short-term price movements. Scalpers hold positions for only a few seconds to several minutes and aim to make multiple trades per day to capture small price differences. Scalping is a highly active and intensive form of trading that requires a high level of focus, speed, and discipline. The profits from scalping are typically small, but they can add up over time if done consistently and effectively. This style of trading is not suitable for everyone and carries a higher level of risk compared to other strategies.
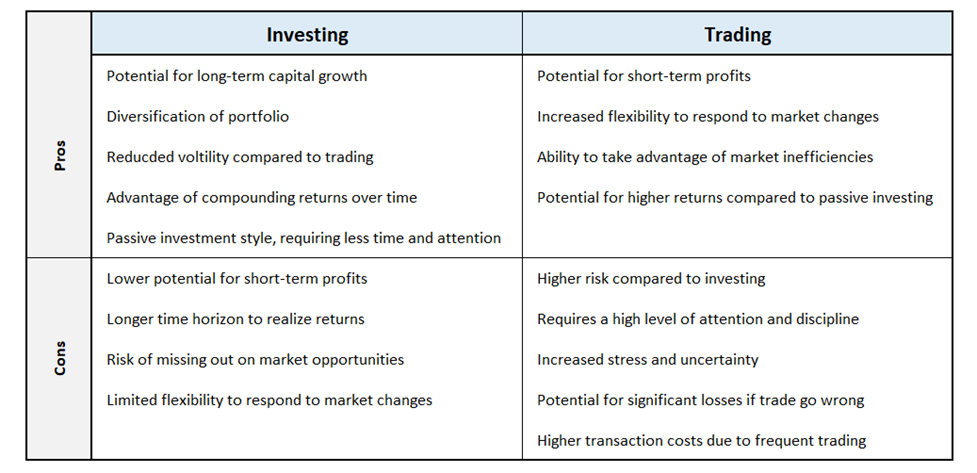
Major Differences between Investing and Trading
Investing and trading are two distinct investment strategies that differ in the following aspects:
Risk involved: Investing generally involves taking on a lower level of risk compared to trading, as investments are held for a longer period of time and are expected to provide steady growth over time. Trading, on the other hand, involves a higher level of risk as traders aim to make quick profits from short-term price movements.
Capital requirement: Investing often requires a larger capital outlay as investments are made for the long term. Investors may be locked into an investment for a longer horizon, whereas traders can quickly liquidate positions as required. Trading can be done with a smaller capital base as traders aim to make multiple trades with small profits.
Analysis style: Investing involves a fundamental analysis approach that considers a company's financial and operational metrics, as well as macroeconomic trends and conditions. Trading, on the other hand, often relies on technical analysis and chart patterns to make decisions.
Capital growth: Investing is typically focused on long-term capital growth through the appreciation of assets. Trading, on the other hand, aims to generate profits from short-term price movements or mispricing in the market.
Psychology: Investing requires patience, discipline, and a long-term perspective, as investments are made for the purpose of steady growth over time. Trading, on the other hand, requires a quicker decision-making ability and the ability to handle high levels of stress and uncertainty.
Final Words
In summary, whether investing or trading is "better" depends on an individual's financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment style.
For long-term financial goals and a lower risk tolerance, investing may be more appropriate, as it focuses on the steady growth of capital over a longer period of time. And, for those with higher risk tolerance and a shorter-term focus, trading may be a more suitable strategy, as it aims to generate profits from short-term price movements.
Ultimately, the best strategy is the one that aligns with an individual's financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment style. It is important for investors to carefully consider their options and make informed decisions based on their own financial circumstances.
